利用 Rxi-SVOCms 色谱柱
改进半挥发物方法性能
- 凭借良好的峰形、响应和分离度,可确保分析准确度和灵敏度。
- 高惰性、超低流失色谱柱,可提供出色的痕量活性化合物分析结果。
- 通过稳定的校准和一致的柱间性能提升生产率。
半挥发物方法是环境测试程序的重要组成部分,但由于目标分析物很多且包含不同类型的反应性化合物,实验室难以实现高效运行这些方法。为了准确地报告半挥发物,特别是反应性物质,必须使用高惰性色谱柱,以确保得到良好的色谱和稳定的校准。Rxi-SVOCms 色谱柱专为半挥发物分析而设计,具有优化的选择性、出色的惰性和极低流失等特点,可提高分析性能和实验室生产率。
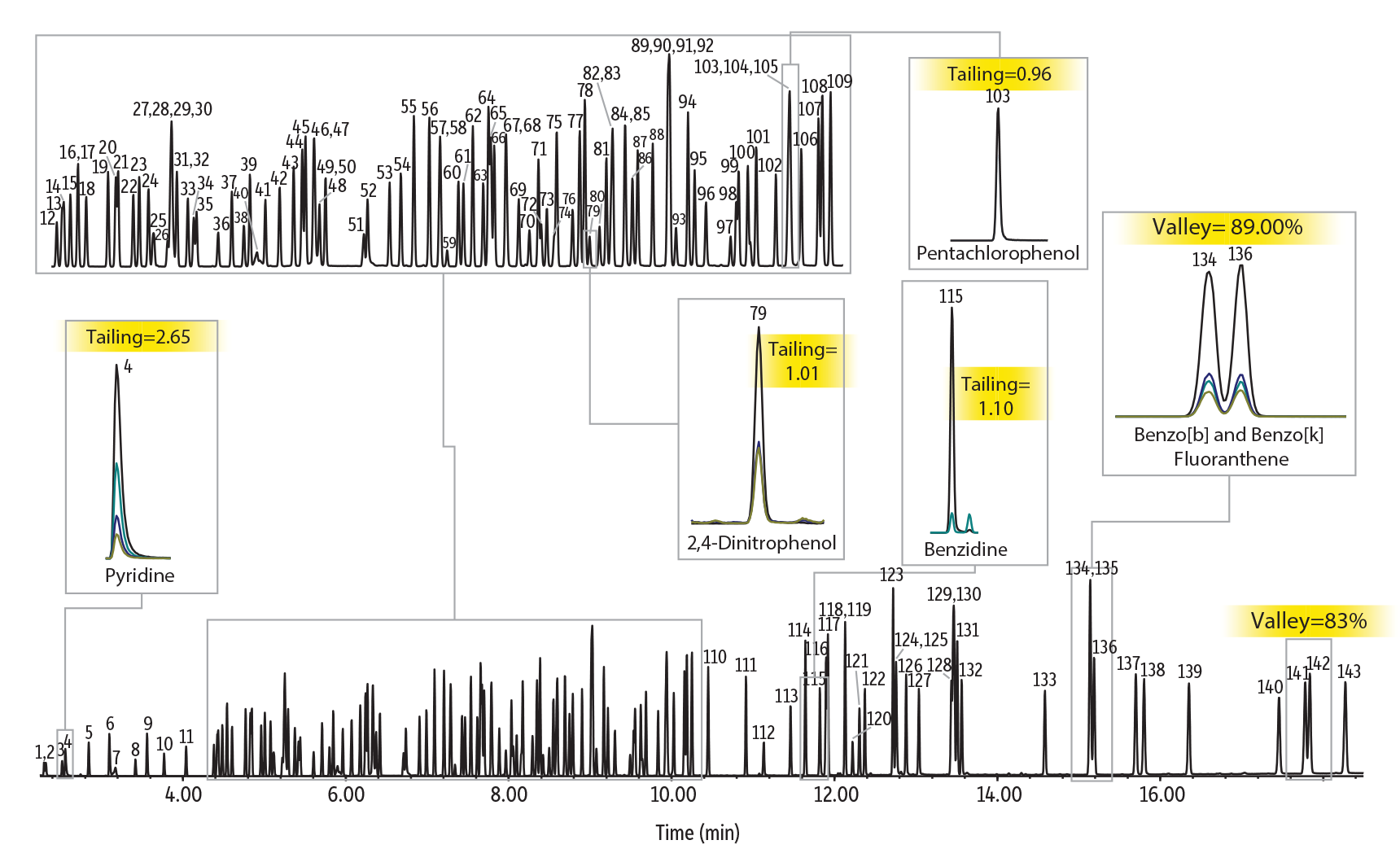
如下所示,各种反应性化合物都能获得良好的峰形和响应,包括酸性苯酚(五氯苯酚和二硝基苯酚)和胺(联苯胺和吡啶),应用半挥发物方法时这些分析物通常会造成问题。此处推荐使用分流进样,因为这样可以最大限度地减少实际样品分析过程中由基质组分产生的活性位点积累。由于 Rxi-SVOCms 色谱柱惰性高,最大限度地减少了拖尾现象,从而改善了峰形和响应,使精确积分变得容易和可靠。色谱性能更好,灵敏度和再现性更佳,因此校准时间间隔更长,在需要重新校准之前可以分析更多样品。
除了碱性和酸性反应性化合物分析性能提高外,对半挥发物方法中最麻烦的中性多环芳烃 (PAH) 也有出色的分离度。Rxi-SVOCms 色谱柱能较好地分离临界物质对,例如茚并[1,2,3-cd]芘和二苯并[a,h]蒽以及苯并[b]荧蒽和苯并[k]荧蒽,可实现阳性鉴别和准确报告。凭借始终如一的优质色谱,Rxi-SVOCms 色谱柱可助力实验室有效改善半挥发物方法性能。
图 1: Rxi-SVOCms 色谱柱的色谱性能出色,分析易产生问题的化合物时可产生良好峰形和分离度。
| Column | Rxi-SVOCms, 30 m, 0.25 mm ID, 0.25 µm (cat.# 16623) |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | Revised SV internal standard mix (cat.# 31886) |
| Revised B/N surrogate mix (cat.# 31888) | |
| Acid surrogate mix (cat.# 31063) | |
| 8270 MegaMix standard (cat.# 31850) | |
| 8270 Benzidines mix (cat.# 31852) | |
| Benzoic acid (cat.# 31879) | |
| Appendix IX mix #1, Revised (cat.# 32459) | |
| Appendix IX mix #2 (cat.# 31806) | |
| Diluent: | Dichloromethane |
| Conc.: | 20 ng/µL |
| Injection | |
| Inj. Vol.: | 1 µL split (split ratio 10:1) |
| Liner: | Topaz 4.0 mm ID single taper inlet liner with wool (cat.# 23303) |
| Inj. Temp.: | 250 °C |
| Split Vent Flow Rate: | 12 mL/min |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 40 °C (hold 0.5 min) to 280 °C at 20 °C/min to 330 °C at 6 °C/min (hold 4 min) |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant flow |
| Flow Rate: | 1.2 mL/min |
| Detector | MS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode: | Scan | ||||||||
| Scan Program: | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Transfer Line Temp.: | 280 °C | ||||||||
| Analyzer Type: | Quadrupole | ||||||||
| Source Type: | Extractor | ||||||||
| Extractor Lens: | 6 mm ID | ||||||||
| Source Temp.: | 330 °C | ||||||||
| Quad Temp.: | 150 °C | ||||||||
| Electron Energy: | 70 eV | ||||||||
| Solvent Delay Time: | 1.55 min | ||||||||
| Tune Type: | DFTPP | ||||||||
| Ionization Mode: | EI | ||||||||
| Instrument | Agilent 7890B GC & 5977A MSD | ||||||||
| Sample Preparation | Samples were aliquoted into amber 2 mL, 9 mm short-cap, screw-thread vials (cat.# 21143) containing glass Big Mouth inserts (cat.# 21782) and sealed with 2.0 mL, 9 mm short-cap, screw-vial closures (cat.# 23842). | ||||||||

